[딥러닝] TensorFlow 기반 신경망 실습
TensorFlow
TensorFlow 프레임 워크 개요
- TensorFlow : Google에서 개발한 딥러닝/수치 계산용 오픈소스 라이브러리
- 파이썬, C++ API 제공
- 계산은 내부적으로 C/C++ 기반으로 매우 빠르다.
- GPU/TPU/모바일(Android 등) 환경에서도 사용 가능하다.
- 데이터 플로우 그래프(Data Flow Graph) 구조로 모델 구성
주요 구성 요소
데이터 플로우 그래프(Data Flow Graph)
import tensorflow as tf
a = tf.constant(2, name='a')
b = tf.constant(3, name='b')
c = tf.add(a, b, name='c')
d = tf.multiply(b,c,name='d')
with tf.Session() as sess:
result = sess.run(c)
print(result)
위 프로그램의 데이터 플로우 그래프 -> 텐서보드(Tensorboard)를 통해 확인 가능하다.
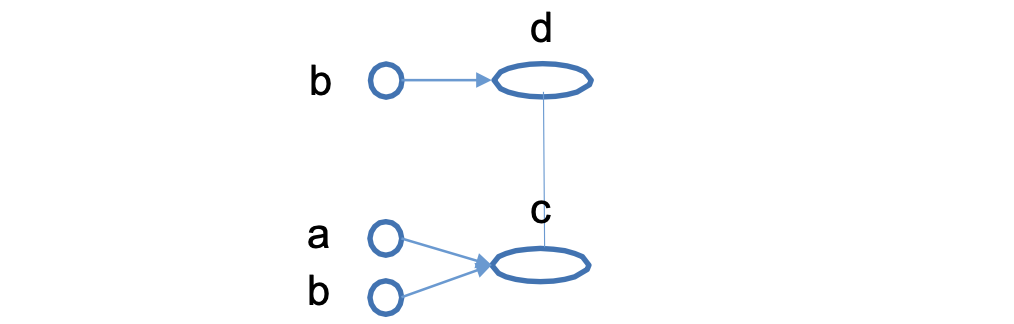
- Operation(Op) : 노드, 수학적 계산을 수행하는 단위로 하나 이상의 텐서를 받아 계산을 수행하고 결과를 하나 이상의 텐서로 변환한다.
- Tensor : 간선, 데이터(다차원 배열) 전달 단위. 모든 데이터는 텐서를 통해 표현된다.
- Session : 그래프를 실행하기 위한 런타임 환경
- Variables : 학습 가능한 가중치 저장(초기화 필수). 그래프 실행 시 파라미터를 저장하고 갱신하기 위해 사용한다.
- Variable : 모델의 학습 가능한 변수를 정의할 때 Variable을 사용한다. 가중치, 편향 등의 파라미터를 저장하는 데 사용된다.
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([4,1]), name=“weight”)
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1]), name=“bias”)
- Placeholder : 데이터 플로우 그래프 실행 시 데이터(텐서)를 전달하기 위해 사용한다. 그래프 실행 시 값이 제공되어야 한다.
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
z = tf.multiply(x,y)
sess.run(z, feed_dict=[x: 3, y:4])
텐서(Tensor)
텐서플로우에서 사용하는 기본 자료형인 다차원 배열을 의미한다. rank, shape, type 세가지 속성을 가진다.
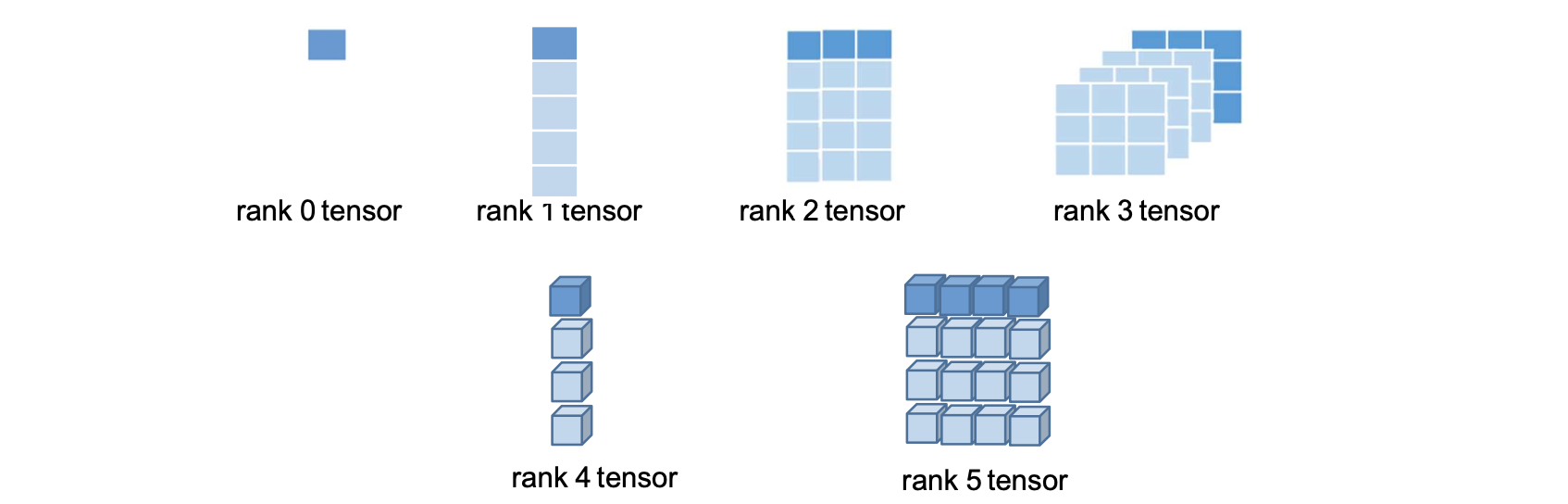
Rank
rank : 텐서의 차원수 (dimension, order, degree 라고도 한다.)
- rank 0 텐서 : 스칼라 값
- rank 1 텐서 : 1차원 배열(rank 0 텐서의 배열)
- rank 2 텐서 : 2차원 배열(rank 1 텐서의 배열)
- rank n 텐서 : n차원 배열(rank n-1 텐서의 배열)
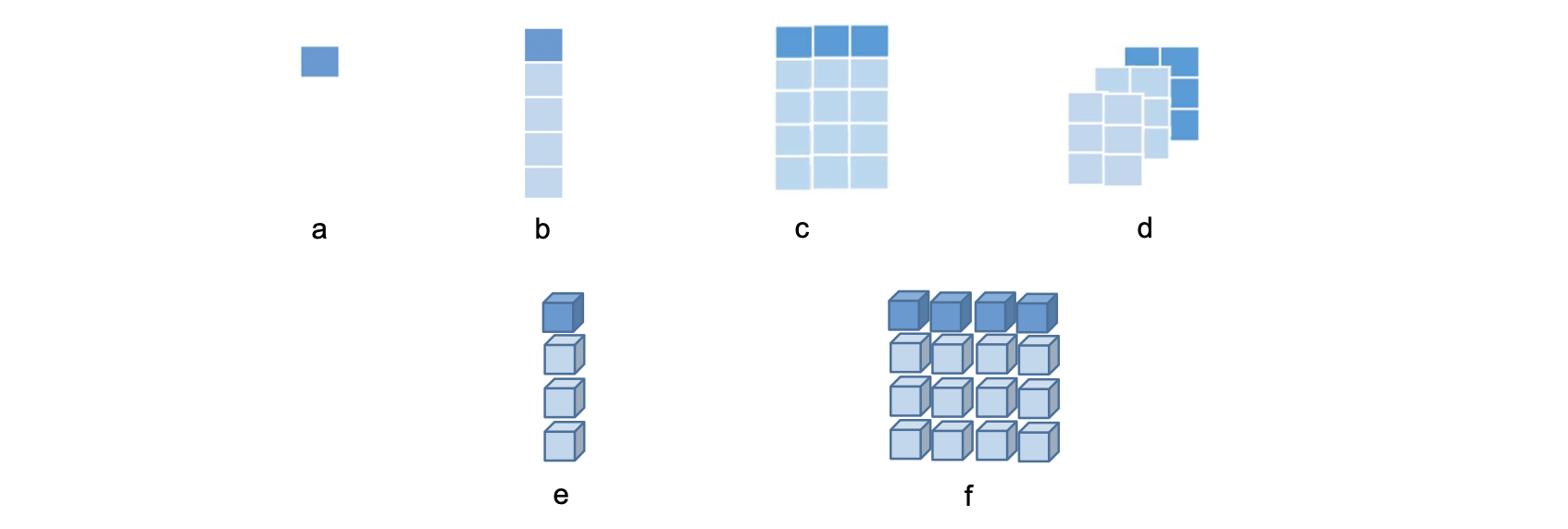
Shape
텐서의 구조, 각 차원의 크기를 의미한다.
- shape[m] : rank1인 텐서로 원소를 m개 가지고 있다.
- shape[ i1, i2,…, ik ] : shape[ i2,…, ik ]인 원소를 i1개 가지고 있음
- 예:
- b = [6,3,5,2,7] -> b의 shape : [5]
- c = [[1,2,3],[3,6,1],[5,8,2],[6,1,2],[8,2,3]] -> c의 shape : [5,3]
- d = [[[1,2],[3,4],[4,5]], [[3,2],[5,7],[2,8]], [[5,1],[5,4],[8,2]]] -> d의 shape: [3,3,2]
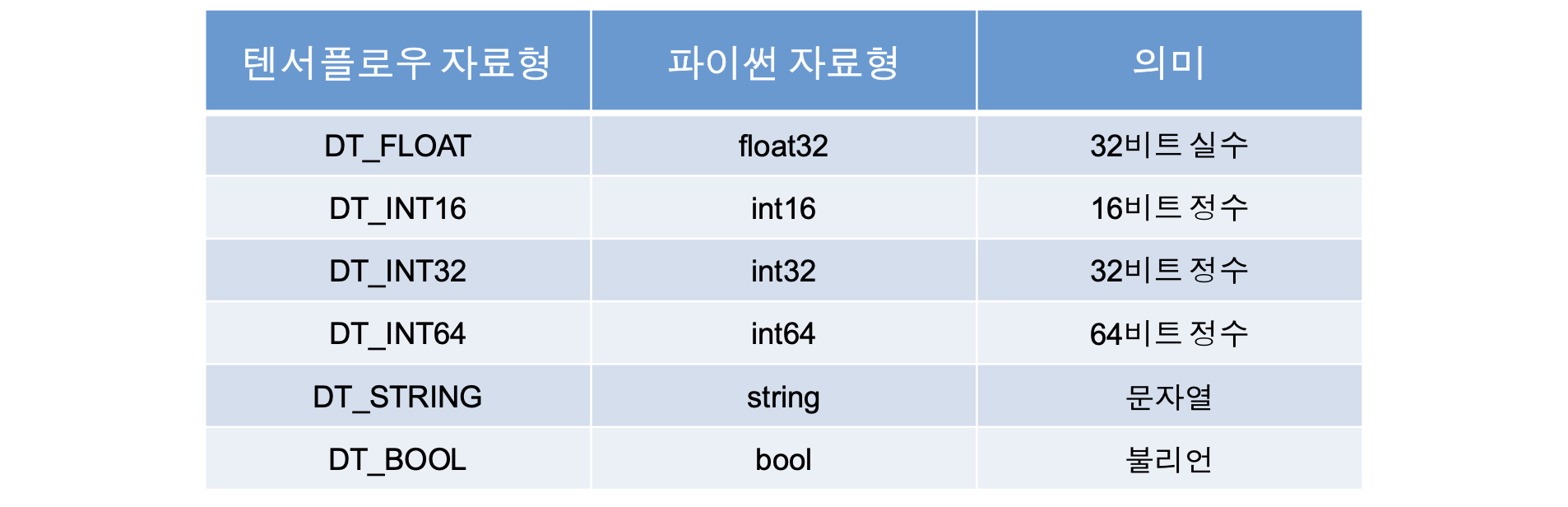
Type
텐서 구성 원소의 자료형
Tensor 변환 연산
shape, size, rank
- shape : 텐서의 shape 정보 확인
- size : 텐서의 크기 확인
- rank : 텐서의 rank 확인
import tensorflow as tf
t = tf.constant([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
print("Shape:", tf.shape(t).numpy()) # [2, 3]
print("Size:", tf.size(t).numpy()) # 6
print("Rank:", tf.rank(t).numpy()) # 2
reshape
텐서의 원소는 유지하면서 구조(shape)를 변경
t = tf.constant([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
reshaped = tf.reshape(t, [2, 3])
print(reshaped.numpy()) # [[1 2 3], [4 5 6]]
squeeze
크기 1인 차원을 제거(불필요한 차원을 없애서 연산을 간소화)
t = tf.constant([[[1], [2], [3]]]) # shape (1, 3, 1)
print("Before:", t.shape)
squeezed = tf.squeeze(t)
print("After:", squeezed.shape) # shape (3,)
expand_dims
원하는 위치에 차원을 추가(모델에 넣기 전에 차원 맞추기 등)
t = tf.constant([1, 2, 3])
print("Original:", t.shape)
expanded = tf.expand_dims(t, axis=0) # shape (1, 3)
print("Expanded:", expanded.shape)
slice
텐서의 일부분을 잘라내기
t = tf.constant([[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12]])
sliced = tf.slice(t, [0, 1], [2, 2]) # 시작점: (0,1), 크기: (2,2)
print(sliced.numpy()) # [[2,3],[6,7]]
split
텐서를 지정된 축을 따라 나누기
t = tf.constant([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6], [7, 8]])
split_t = tf.split(t, num_or_size_splits=2, axis=0)
for part in split_t:
print(part.numpy())
tile
텐서를 복제하여 반복한 새로운 텐서 생성
t = tf.constant([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
tiled = tf.tile(t, [2, 3]) # 행 2번, 열 3번 반복
print(tiled.numpy())
concat
텐서들을 지정한 축을 기준으로 연결
a = tf.constant([[1, 2]])
b = tf.constant([[3, 4]])
c = tf.concat([a, b], axis=0) # 행 방향 연결
print(c.numpy()) # [[1, 2], [3, 4]]
reverse
지정된 축을 기준으로 원소 순서 뒤집기
t = tf.constant([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
reversed = tf.reverse(t, axis=[1])
print(reversed.numpy()) # [[3, 2, 1], [6, 5, 4]]
transpose
행과 열을 바꾸는 연산, 다차원일 경우 지정한 순열로 축 순서를 변경한다.
t = tf.constant([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
transposed = tf.transpose(t)
print(transposed.numpy()) # [[1,4],[2,5],[3,6]]
gather
지정한 인덱스의 원소만 추출하는 고급 인덱싱 기능
t = tf.constant([10, 20, 30, 40, 50])
g = tf.gather(t, [0, 2, 4])
print(g.numpy()) # [10, 30, 50]
Tensor 산술 연산
기본 산술 연산
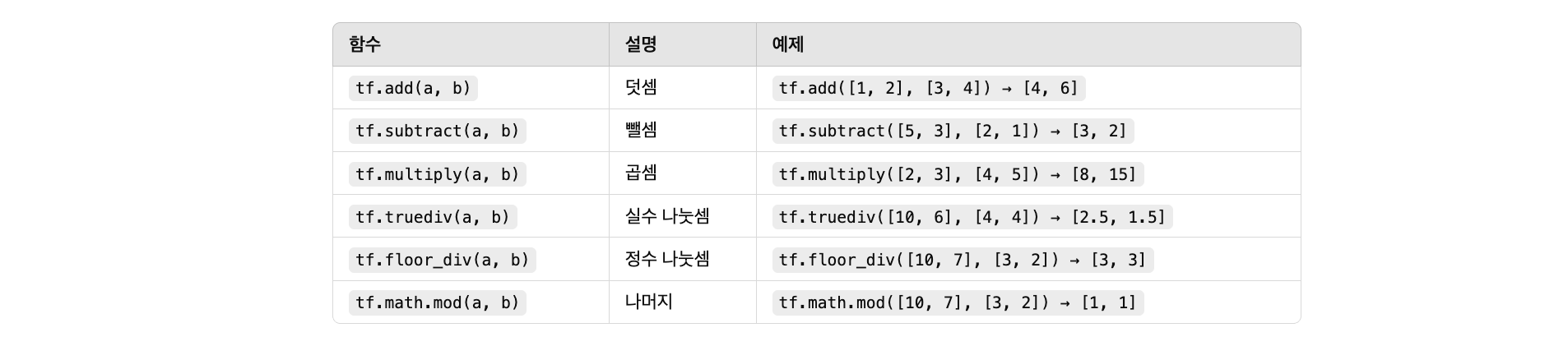
수학/수치 연산
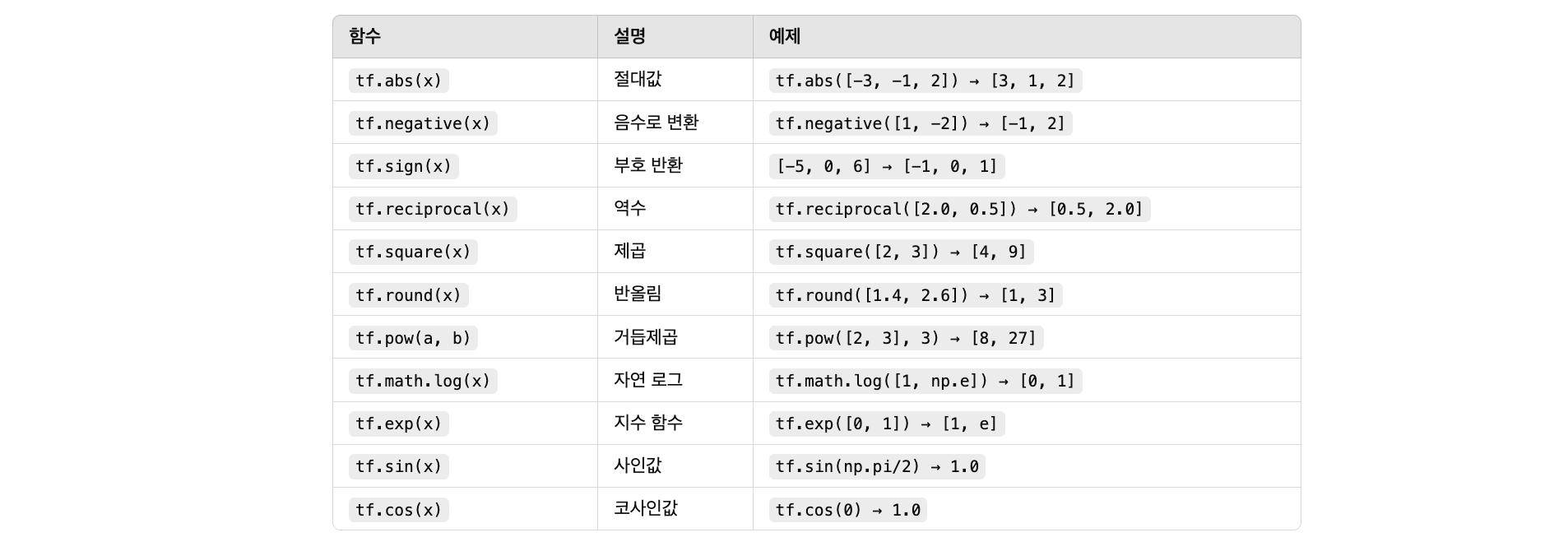
실습용 예제 코드
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
a = tf.constant([2.0, 4.0])
b = tf.constant([3.0, 2.0])
print("덧셈:", tf.add(a, b).numpy()) # [5. 6.]
print("뺄셈:", tf.subtract(a, b).numpy()) # [-1. 2.]
print("곱셈:", tf.multiply(a, b).numpy()) # [6. 8.]
print("실수 나눗셈:", tf.truediv(a, b).numpy()) # [0.6666, 2.0]
print("정수 나눗셈:", tf.floor_div(tf.cast(a, tf.int32), tf.cast(b, tf.int32)).numpy()) # [0 2]
print("나머지:", tf.math.mod(a, b).numpy()) # [2. 0.]
print("절대값:", tf.abs(tf.constant([-3, 4])).numpy()) # [3 4]
print("음수변환:", tf.negative(a).numpy()) # [-2, -4]
print("부호:", tf.sign(tf.constant([-5, 0, 6])).numpy()) # [-1 0 1]
print("역수:", tf.reciprocal(tf.constant([2.0, 0.5])).numpy()) # [0.5, 2.0]
print("제곱:", tf.square(a).numpy()) # [4. 16.]
print("반올림:", tf.round(tf.constant([1.4, 2.6])).numpy()) # [1. 3.]
print("거듭제곱:", tf.pow(a, b).numpy()) # [8. 16.]
print("로그:", tf.math.log(tf.constant([1.0, np.e])).numpy()) # [0. 1.]
print("지수:", tf.exp(tf.constant([0.0, 1.0])).numpy()) # [1. e]
print("sin(pi/2):", tf.sin(np.pi / 2).numpy()) # 1.0
print("cos(0):", tf.cos(0.0).numpy()) # 1.0
Tensor 축약 연산
축약 연산(reduction) : 텐서의 특징 축(axis)을 따라 연산을 적용하여 크기를 줄이는 함수이다.
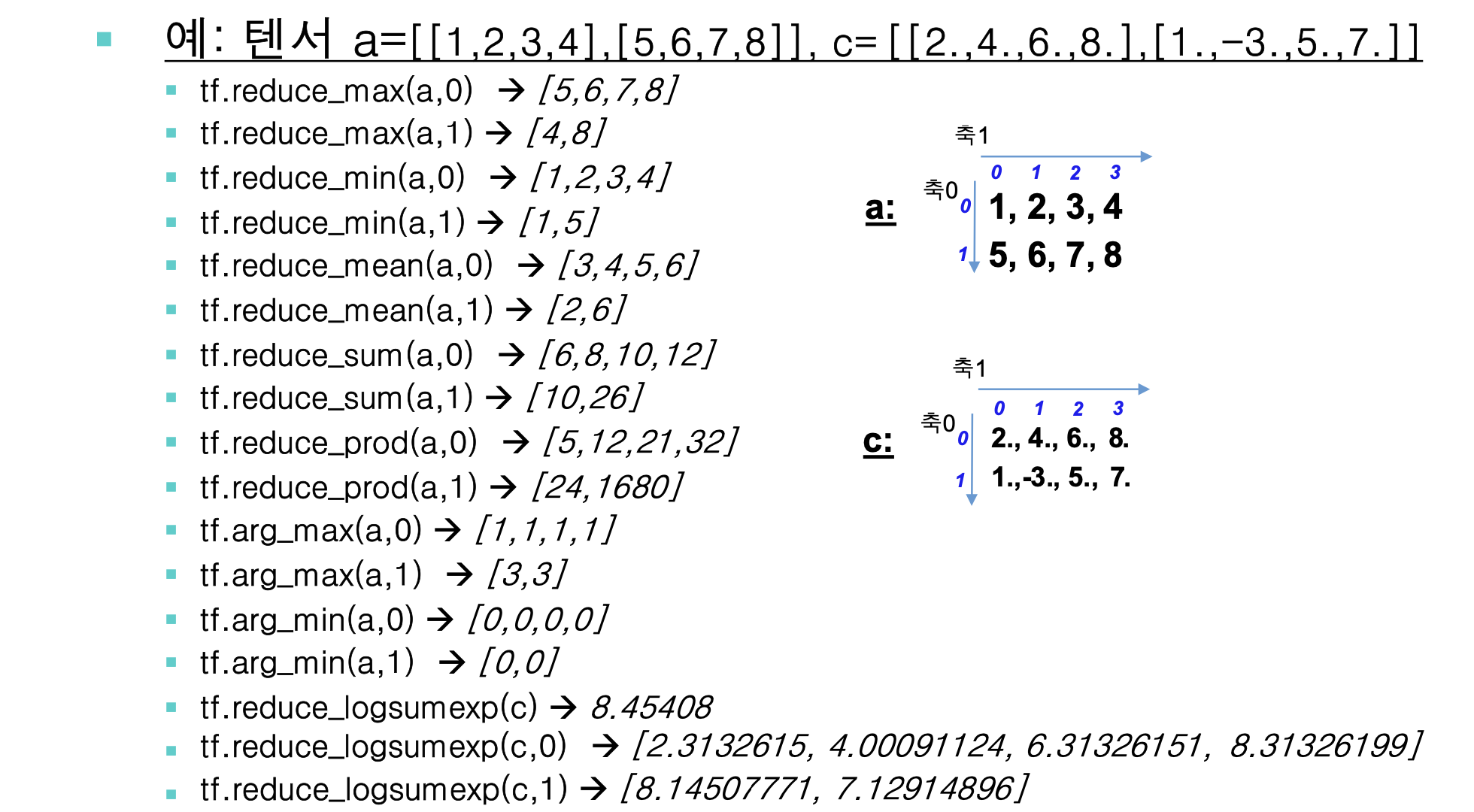
실습 코드
import tensorflow as tf
t = tf.constant([[1, 3], [5, 2]])
print("Max (전체):", tf.reduce_max(t).numpy())
print("Max (열):", tf.reduce_max(t, axis=0).numpy())
print("Min (행):", tf.reduce_min(t, axis=1).numpy())
print("Mean (전체):", tf.reduce_mean(t).numpy())
print("Sum (행):", tf.reduce_sum(t, axis=1).numpy())
print("Prod (열):", tf.reduce_prod(t, axis=0).numpy())
print("Argmax (열):", tf.argmax(t, axis=0).numpy())
print("Argmin (행):", tf.argmin(t, axis=1).numpy())
t_float = tf.constant([[1.0, 2.0], [3.0, 4.0]])
print("LogSumExp (행):", tf.reduce_logsumexp(t_float, axis=1).numpy())
Tensor 행렬 연산
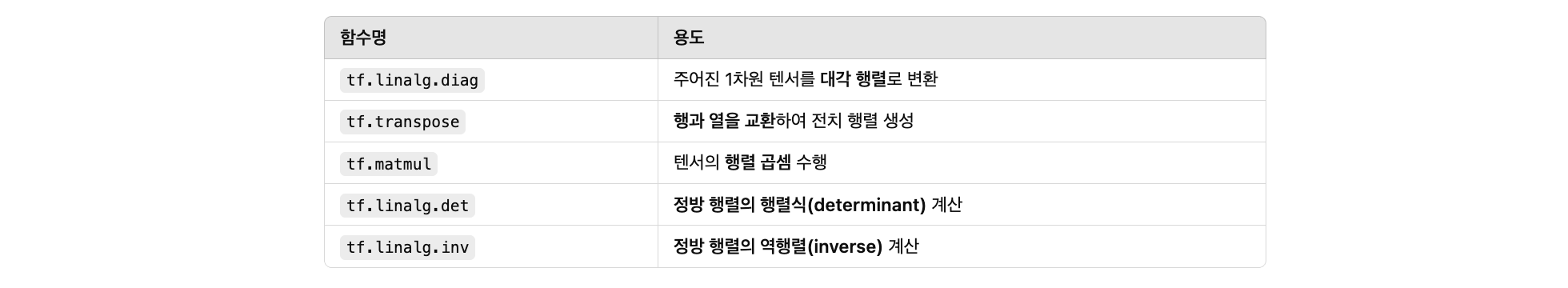

import tensorflow as tf
# 1. diag: 대각 행렬 생성
x = tf.constant([1, 2, 3])
diag_matrix = tf.linalg.diag(x)
print("1. 대각 행렬 (diag):\n", diag_matrix.numpy())
# 2. transpose: 전치 행렬
a = tf.constant([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
transposed = tf.transpose(a)
print("\n2. 전치 행렬 (transpose):\n", transposed.numpy())
# 3. matmul: 행렬 곱셈
b = tf.constant([[2, 0], [1, 2]])
matmul_result = tf.matmul(a, b)
print("\n3. 행렬 곱셈 (matmul):\n", matmul_result.numpy())
# 4. matrix_determinant: 행렬식
square_matrix = tf.constant([[1.0, 2.0], [3.0, 4.0]])
det = tf.linalg.det(square_matrix)
print("\n4. 행렬식 (det):", det.numpy())
# 5. matrix_inverse: 역행렬
inv_matrix = tf.constant([[4.0, 7.0], [2.0, 6.0]])
inverse = tf.linalg.inv(inv_matrix)
print("\n5. 역행렬 (inv):\n", inverse.numpy())
Tensor 기타 유용한 함수
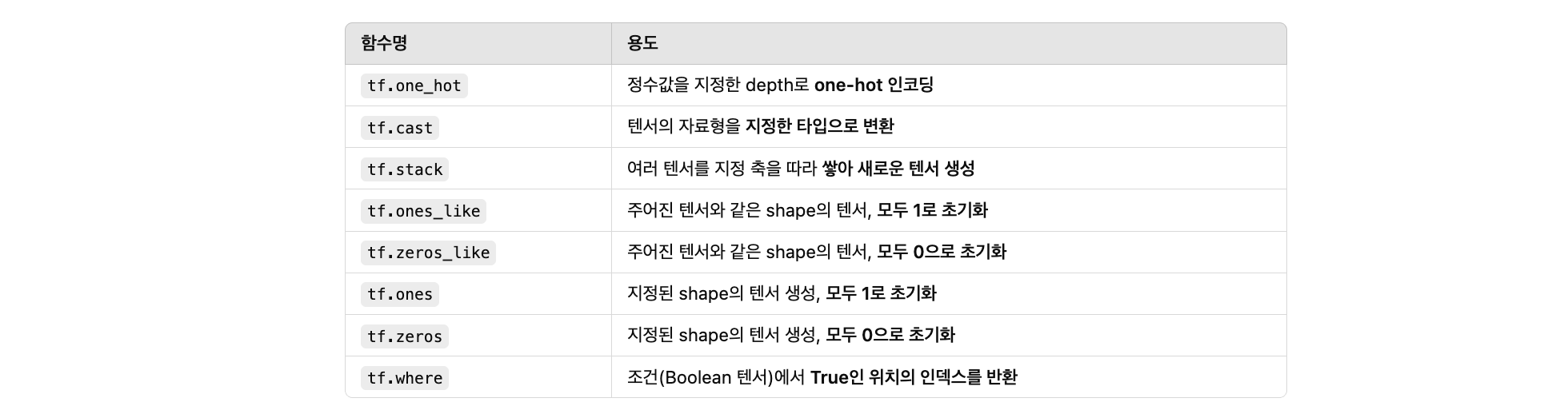
import tensorflow as tf
# 1. one_hot
labels = [0, 2, 1]
one_hot = tf.one_hot(labels, depth=3)
print("1. one_hot:\n", one_hot.numpy())
# 2. cast
float_tensor = tf.constant([1.2, 3.4])
int_tensor = tf.cast(float_tensor, tf.int32)
print("\n2. cast to int:\n", int_tensor.numpy())
# 3. stack
a = tf.constant([1, 2])
b = tf.constant([3, 4])
stacked = tf.stack([a, b], axis=0)
print("\n3. stack (axis=0):\n", stacked.numpy())
# 4. ones_like & zeros_like
base = tf.constant([[5, 6], [7, 8]])
ones = tf.ones_like(base)
zeros = tf.zeros_like(base)
print("\n4. ones_like:\n", ones.numpy())
print(" zeros_like:\n", zeros.numpy())
# 5. ones & zeros
o = tf.ones([2, 3])
z = tf.zeros([3])
print("\n5. ones:\n", o.numpy())
print(" zeros:\n", z.numpy())
# 6. where (Boolean mask → 위치 추출)
condition = tf.constant([[True, False], [False, True]])
indices = tf.where(condition)
print("\n6. where (True 위치):\n", indices.numpy())
난수 생성 함수
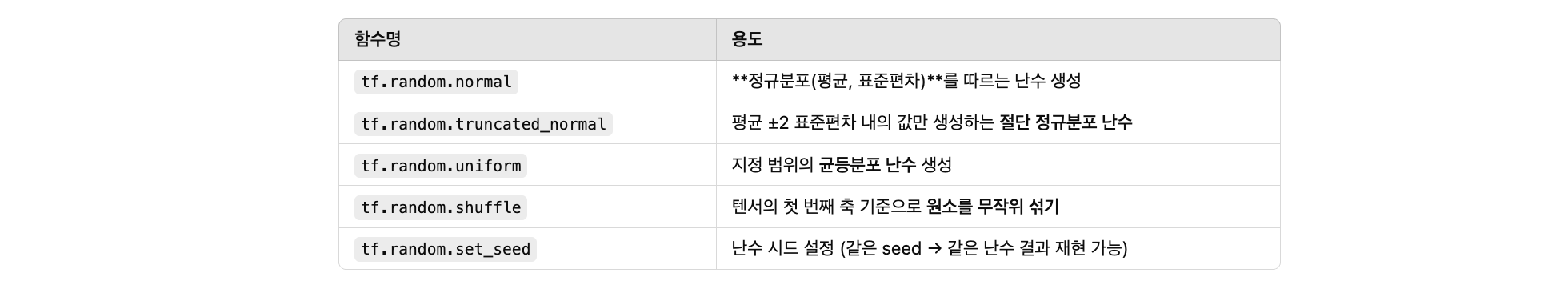
import tensorflow as tf
# 시드 설정
tf.random.set_seed(42)
# 1. random_normal: 정규분포 난수 생성 (mean=0, stddev=1)
normal = tf.random.normal(shape=[2, 3], mean=0.0, stddev=1.0)
print("1. random_normal:\n", normal.numpy())
# 2. truncated_normal: 절단된 정규분포 (mean ± 2std 바깥 값 제거됨)
trunc_normal = tf.random.truncated_normal(shape=[2, 3], mean=0.0, stddev=1.0)
print("\n2. truncated_normal:\n", trunc_normal.numpy())
# 3. random_uniform: 균등 분포 난수 생성 (0~10 사이 실수)
uniform = tf.random.uniform(shape=[2, 3], minval=0, maxval=10)
print("\n3. random_uniform:\n", uniform.numpy())
# 4. random_shuffle: 첫 번째 축 기준으로 순서 섞기
original = tf.constant([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
shuffled = tf.random.shuffle(original)
print("\n4. random_shuffle:\n", shuffled.numpy())
# 5. set_random_seed: 위에서 이미 사용됨 (재현성 보장)
# 같은 seed를 사용하면 결과가 동일함