[자료구조] 큐(Queue)
큐(Queue)란?
- 큐(queue)는 선입선출(FIFO, First In First Out)방식으로 동작하는 선형 자료구조이다. 즉, 큐에 먼저 추가된 데이터가 먼저 제거된다. 이는 현실에서 줄을 서는 방식과 유사하다.
큐의 ADT(추상 자료형)
void QueueInit(Queue *pqueue);
- 큐를 초기화하는 함수
- 큐를 사용하기 전에 반드시 호출해야 한다.
int QIsEmpty(Queue *pqueue);
- 큐가 비어있는지 확인하는 함수
- 큐가 비어있으면 TRUE(1), 그렇지 않으면 FALSE(0) 반환
void QPush(Queue *pqueue, Data data);
- 큐의 뒤쪽(Rear)에 데이터를 추가하는 함수
Data QPop(Queue *pqueue);
- 큐의 앞쪽(Front)에서 데이터를 제거하는 함수
- 제거된 데이터는 반환된다.
- 큐가 비어있는 상태에서 호출하면 오류가 발생할 수 있다.
Data QPeek(Queue *pqueue);
- 큐의 앞쪽(Front)에 위치한 데이터를 반환하지만 제거하지 않는 함수
큐의 특징
- 선입선출(FIFO) : 먼저 들어온 데이터가 먼저 제거된다.
- 제한적인 접근 : 큐의 맨 앞(Front)과 맨 뒤(Rear)에서만 데이터 추가/삭제가 가능하다.
- 동적 크기 : 배열 또는 연결 리스트로 구현되며, 필요에 따라 크기가 확장될 수 있다.
큐의 동작(Push, Pop)
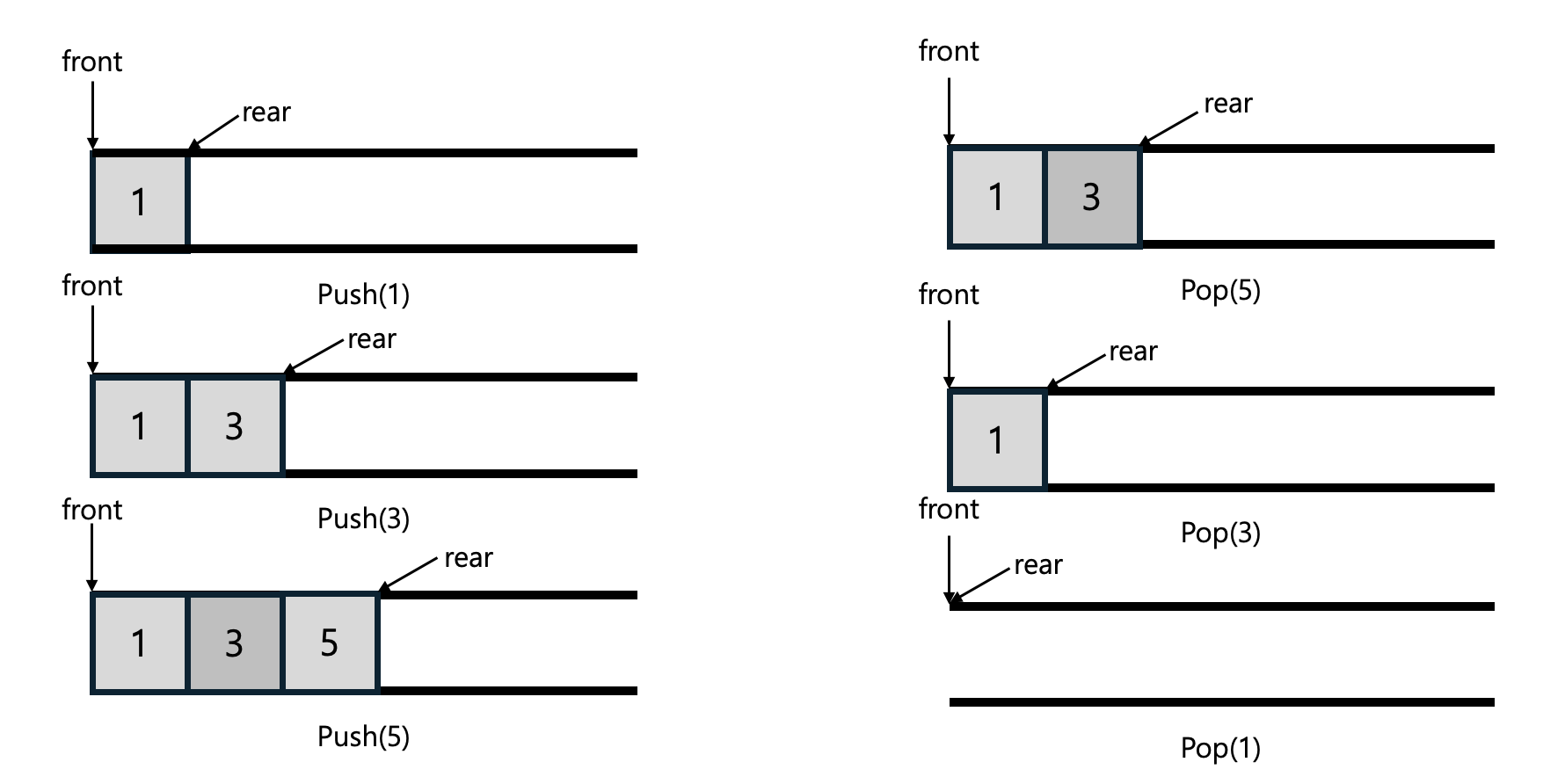
큐의 배열 기반 구현
배열 기반 큐는 배열을 사용하여 데이터를 저장하고, front와 rear 변수를 통해 큐의 상태를 관리한다. 이 구현에서는 큐의 크기를 QUEUE_LEN으로 설정하며, fornt와 rear는 데이터의 위치를 나타낸다.
헤더 파일의 정의(ArrayBaseQueue.h)
#ifndef __AB_QUEUE_H_
#define __AB_QUEUE_H_
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define QUEUE_LEN 100
typedef int Data;
typedef struct _arrayQueue {
Data queArr[QUEUE_LEN]; // 배열 기반 큐
int front; // 앞쪽 위치
int rear; // 뒤쪽 위치
} ArrayQueue;
typedef ArrayQueue Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue *pqueue); // 큐 초기화
int QIsEmpty(Queue *pqueue); // 큐가 비어있는지 확인
void QPush(Queue *pqueue, Data data); // 데이터 삽입 (rear)
Data QPop(Queue *pqueue); // 데이터 삭제 (front)
Data QPeek(Queue *pqueue); // 큐의 front 데이터 반환 (제거X)
#endif
배열 기반 큐의 구현
typedef struct _arrayQueue {
Data queArr[QUEUE_LEN]; // 배열 기반 큐
int front; // 앞쪽 위치
int rear; // 뒤쪽 위치
} ArrayQueue;
위 구조체 멤버 중 초기화할 멤버는 앞쪽을 가리키는 front와 뒤를 가리키는 rear 두가지이다. 따라서 QueueInit 함수는 다음과 같이 정의된다.
void QueueInit(Queue *pqueue){
pqueue->front = 0;
pqueue->rear = 0;
}
큐의 초기 상태는 아무 것도 없는 상태이므로, queue의 앞쪽을 나타내는 front와 queue의 뒤쪽을 나타내는 rear의 위치가 같음으로 표현한다.
이어서 QIsEmpty 함수의 정의이다. 이 함수는 큐가 비어있는지 확인할 때 호출하는 함수이다. 큐가 비어있는 경우 큐의 front와 rear가 같은 위치를 가리키게된다.
int QIsEmpty(Queue *pqueue){
if(pqueue->front == pqueue->rear)
return TRUE;
else
return FALSE;
}
다음은 큐의 핵심인 QPush와 QPop 함수이다.
void QPush(Queue *pqueue, Data data) {
if ((pqueue->rear + 1) % QUEUE_LEN == pqueue->front) {
printf("Queue Memory Error!\n");
exit(-1);
}
pqueue->rear = (pqueue->rear + 1) % QUEUE_LEN;
pqueue->queArr[pqueue->rear] = data;
}
Data QPop(Queue *pqueue) {
if (QIsEmpty(pqueue)) {
printf("Queue Memory Error!\n");
exit(-1);
}
pqueue->front = (pqueue->front + 1) % QUEUE_LEN;
return pqueue->queArr[pqueue->front];
}
push의 경우는 rear의 위치가 한칸 증가하여 데이터 개수가 증가함을 표현한다.
데이터 삭제의 경우 배열 기반이므로 front를 증가시켜주어 삭제됨을 표현한다. front를 그대로 유지할 경우 뒤쪽 데이터를 모두 한칸씩 이동시켜야하므로 front의 위치를 한칸 증가시켜준다.
다음은 QPeek 함수이다. 해당 함수는 QPop 함수와 달리 반환한 데이터를 소멸시키지 않으므로 다음과 같이 간단히 정의가 가능하다.
Data QPeek(Queue *pqueue) {
if (QIsEmpty(pqueue)) {
printf("Queue Memory Error!\n");
exit(-1);
}
return pqueue->queArr[(pqueue->front + 1) % QUEUE_LEN];
}
전체 코드(배열 기반 큐)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "ArrayBaseQueue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue *pqueue) {
pqueue->front = 0;
pqueue->rear = 0;
}
int QIsEmpty(Queue *pqueue) {
if (pqueue->front == pqueue->rear)
return TRUE;
else
return FALSE;
}
void QPush(Queue *pqueue, Data data) {
if ((pqueue->rear + 1) % QUEUE_LEN == pqueue->front) {
printf("Queue Memory Error!\n");
exit(-1);
}
pqueue->rear = (pqueue->rear + 1) % QUEUE_LEN;
pqueue->queArr[pqueue->rear] = data;
}
Data QPop(Queue *pqueue) {
if (QIsEmpty(pqueue)) {
printf("Queue Memory Error!\n");
exit(-1);
}
pqueue->front = (pqueue->front + 1) % QUEUE_LEN;
return pqueue->queArr[pqueue->front];
}
Data QPeek(Queue *pqueue) {
if (QIsEmpty(pqueue)) {
printf("Queue Memory Error!\n");
exit(-1);
}
return pqueue->queArr[(pqueue->front + 1) % QUEUE_LEN];
}
큐의 연결 리스트 기반 구현
연결 리스트를 사용하면 크기가 동적으로 조정되므로, 배열 기반 큐의 고정된 크기 문제를 해결할 수 있다. 이 구현에서는 노드(Node)를 생성하고, front와 rear가 각각 큐의 시작과 끝을 가리키도록 관리한다.
### 헤더 파일의 정의(ListBaseQueue.h)
#ifndef __LB_QUEUE_H_
#define __LB_QUEUE_H_
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
typedef int Data;
typedef struct _node {
Data data;
struct _node *next;
} Node;
typedef struct _listQueue {
Node *front; // 가장 앞쪽 노드
Node *rear; // 가장 뒤쪽 노드
} ListQueue;
typedef ListQueue Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue *pqueue); // 큐 초기화
int QIsEmpty(Queue *pqueue); // 큐가 비어있는지 확인
void Enqueue(Queue *pqueue, Data data); // 데이터 삽입 (rear)
Data Dequeue(Queue *pqueue); // 데이터 삭제 (front)
Data QPeek(Queue *pqueue); // 큐의 front 데이터 반환 (제거X)
#endif
연결 리스트 기반 큐의 구현
전체 코드(연결 리스트 기반 큐)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "ListBaseQueue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue *pqueue) {
pqueue->front = NULL;
pqueue->rear = NULL;
}
int QIsEmpty(Queue *pqueue) {
if (pqueue->front == NULL)
return TRUE;
else
return FALSE;
}
void QPush(Queue *pqueue, Data data) {
Node *newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
if (QIsEmpty(pqueue))
pqueue->front = newNode;
else
pqueue->rear->next = newNode;
pqueue->rear = newNode;
}
Data QPop(Queue *pqueue) {
if (QIsEmpty(pqueue)) {
printf("Queue Memory Error!\n");
exit(-1);
}
Node *rNode = pqueue->front;
Data rData = rNode->data;
pqueue->front = pqueue->front->next;
free(rNode);
if (pqueue->front == NULL)
pqueue->rear = NULL;
return rData;
}
Data QPeek(Queue *pqueue) {
if (QIsEmpty(pqueue)) {
printf("Queue Memory Error!\n");
exit(-1);
}
return pqueue->front->data;
}